Students will be taking home the journal from this semester and in the spring, they will need their second journal to begin biology. Many have already stored a second journal at school, but please check to make sure you have a new journal on January 7 when we return to school.
Wednesday, December 18, 2013
Monday, December 2, 2013
SAS Density Lab and Upcoming Benchmark
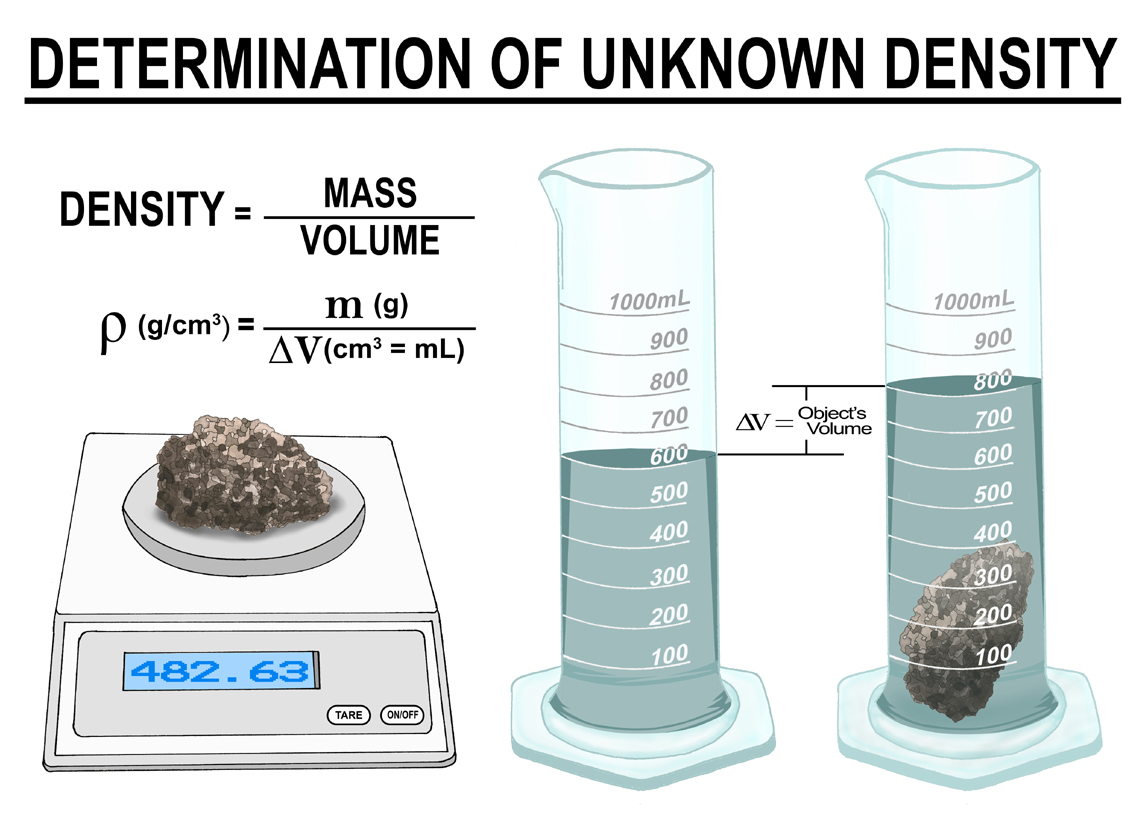
Our classes are currently studying the psychical property of matter known as DENSITY. We are learning to calculate the density of an unknown substance by finding the volume and mass of that object and using the mathematical formula d = m/v
We have done many classroom experiments calculating both mass and volume, and today we are going to use a digital lab to find the density of several unknown objects.
5. The first set of data will be done using the TEST block. Follow the green sheet from here to complete the data table using this site.
BENCHMARK over CHEMISTRY will be on December 18
This covers the journal from page 75 (or close) to current work.
We have done many classroom experiments calculating both mass and volume, and today we are going to use a digital lab to find the density of several unknown objects.
- You must use Google CHROME (the green, red and yellow icon on the bottom navigation bar) to access this website and begin. http://www.sascurriculumpathways.com/portal/#/search?subjectid=3
- Look at the menu on the LEFT SIDE. Check or click on PROPERTIES OF MATTER.
- Go to the 4th link. It says VLAB: DENSITY
- Go underneath the picture and LOG IN using the below user name (cut and paste if needed):
user: sciencerockz
password: sciencerocks
It will pull up a new window. If needed, click on the image and tell it to run the Java plug in.
5. The first set of data will be done using the TEST block. Follow the green sheet from here to complete the data table using this site.
BENCHMARK over CHEMISTRY will be on December 18
This covers the journal from page 75 (or close) to current work.
Thursday, November 14, 2013
Web Quest and Links
What is an Element?
http://education.jlab.org/qa/atoms_and_elements.html
Difference between compounds and elements
http://education.jlab.org/qa/compound.html
Periodic Table and Elements
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/1/
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/4/
Chemical Symbols
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/3/
Hydrogen Facts
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/edexcel/fuels/oil_refining_fuelsrev8.shtml
http://www.energy4me.org/energy-facts/energy-sources/hydrogen/
Metals
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/5/
Nonmetals
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/6/
Metals vs. Nonmetals
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/7/
After you complete your packet, go to this link:
http://www.sd273.com/lschoener/PSWeb/pdtblwebquest.htm
Use this link to research your favorite element.
http://education.jlab.org/qa/atoms_and_elements.html
Difference between compounds and elements
http://education.jlab.org/qa/compound.html
Periodic Table and Elements
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/1/
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/4/
Chemical Symbols
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/3/
Hydrogen Facts
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/edexcel/fuels/oil_refining_fuelsrev8.shtml
http://www.energy4me.org/energy-facts/energy-sources/hydrogen/
Metals
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/5/
Nonmetals
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/6/
Metals vs. Nonmetals
http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/chemical_material_behaviour/atoms_elements/revision/7/
After you complete your packet, go to this link:
http://www.sd273.com/lschoener/PSWeb/pdtblwebquest.htm
Use this link to research your favorite element.
Wednesday, November 13, 2013
Chemistry - update
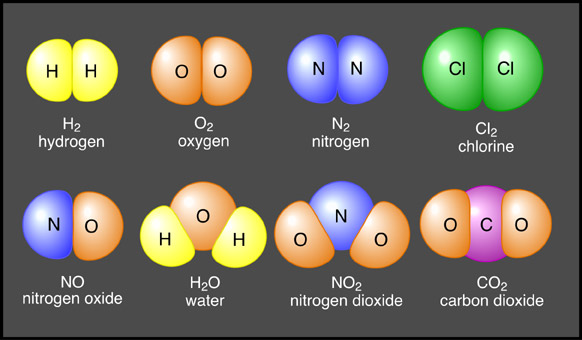
We have started a new unit of study in Chemisty- the study of matter and changes in matter.
So far we have covered the difference between elements and compounds and how to read the element boxes on the periodic table.

We are beginning the study of the physical properties of matter, including mass, volume and density as our main focus. We will need to calculate density using tools and the formula d = m / v, so please work with your student to become proficient in this calculation.
So far we have covered the difference between elements and compounds and how to read the element boxes on the periodic table.


We are beginning the study of the physical properties of matter, including mass, volume and density as our main focus. We will need to calculate density using tools and the formula d = m / v, so please work with your student to become proficient in this calculation.
ONLINE TUTORIAL

Thursday, September 26, 2013
Earth Science Unit - playdough and more
We are in the middle of our earth science unit (pictures to come soon) and one of the things we did was use homemade playdough to model earth's layers. The kids wanted the recipe I used, so I am attaching it for use with adult supervision.
Here are some pictures of the labs and activities that we completed during the Earth Science unit. Our Earth Science TEST is on October 25. It will include earth layers, tectonic plates movement, and rocks and minerals.
Here are some pictures of the labs and activities that we completed during the Earth Science unit. Our Earth Science TEST is on October 25. It will include earth layers, tectonic plates movement, and rocks and minerals.
 |
| We used mapping to prove the movement of the tectonic plates include create of earth's features (including ocean basins, mountains, and trenches). |
 |
| Hot chocolate convection currents - we used heat to create convection currents to move the crust of the hot chocolate. |
 |
| We also used heat with corn syrup to "move" the tectonic plates (lithospheric plates include oceanic and continental crust) |
 |
| We used handmade playdough to create 3-D models of the earth layers. |
 |
| Some classes created 3-D models of earth. |
 |
| another 3-D model |
Sunday, September 22, 2013
Space and Safety Units Concluded
Welcome to 2013-2014. This blog will be updated randomly---basically, when I have time. All our vocabulary is posted in the top tabs and our expectations as well, so you can see what is coming or what is expected during each unit.
Our classroom is a hands-on environment when at all possible. We don't do a lot of teacher lecture and when we do, the kids "talk" to me and answer questions while we do it. Science is a mix of all the subjects, so we include a lot of reading and math because most students need extra practice in that as well.
For the first day of school, we learned how each student learns by doing a multiple intelligences survey so that I knew how to help my students learn. Please ask your student his or her learning styles---they each have more than one.
In general, most of the students preferred art and music and verbal learning---which is great because I do too. We draw a lot of doodles in our journal, listen to music almost every day, and I like to talk---so do they. hehe
To keep track of everything, students are required to keep a composition journal with their notes and activities. They must write neatly and generate a table of contents and match my journal with page numbers and all that we do.
For the first 3.5 weeks of school, we covered Space and reviewed Safety. The journal looks a bit like this:
Our next unit is the Layers of the Earth. Our students are making 2-D and 3-D models of earth layers and they will soon be simulating the movement and shaping of the Earth as well.
Our classroom is a hands-on environment when at all possible. We don't do a lot of teacher lecture and when we do, the kids "talk" to me and answer questions while we do it. Science is a mix of all the subjects, so we include a lot of reading and math because most students need extra practice in that as well.
For the first day of school, we learned how each student learns by doing a multiple intelligences survey so that I knew how to help my students learn. Please ask your student his or her learning styles---they each have more than one.
In general, most of the students preferred art and music and verbal learning---which is great because I do too. We draw a lot of doodles in our journal, listen to music almost every day, and I like to talk---so do they. hehe
To keep track of everything, students are required to keep a composition journal with their notes and activities. They must write neatly and generate a table of contents and match my journal with page numbers and all that we do.
For the first 3.5 weeks of school, we covered Space and reviewed Safety. The journal looks a bit like this:
SAFETY UNIT
SPACE
 |
| each section begins with the expectations that students will be required to know throughout the unit |
 |
| each section has details on the tabs shown at right. Students had to know the physical properties, movement and location of each of these celestial (space) bodies. |
 |
| we concluded our study with a timeline on space exploration. |
Sunday, August 18, 2013
Welcome!
Welcome to Lufkin Middle School and sixth grade science.
I am looking forward to a year filled with new skills and watching you grow your love of science and curiosity about life.
Some of your science supplies will include:
- 2 composition books for journaling (100 pgs. NOT the 70 pg.)
- 1 package markers
- 1 package Crayola Twistable crayons OR map pencil
- $3 lab fee
Throughout the year, we will need these "wish list" items, but they are not necessary:
Parents, middle school is a big step in student accountability. I will focus on helping your student grow many skills along with his or her science skills and I ask that you remember that your student should be the first person to talk to about due dates or project requirements. I will be here to help them build that accountability and responsibility, and I ask that you do the same.
This will be a great year filled with fun experiments and new skills. I look forward to sharing it with all my students.
Mrs. Croll
- Clear tape
- Tissues or Kleenex
- Germ-ex (any brand)
Parents, middle school is a big step in student accountability. I will focus on helping your student grow many skills along with his or her science skills and I ask that you remember that your student should be the first person to talk to about due dates or project requirements. I will be here to help them build that accountability and responsibility, and I ask that you do the same.
This will be a great year filled with fun experiments and new skills. I look forward to sharing it with all my students.
Mrs. Croll
Wednesday, April 24, 2013
Thursday, April 11, 2013
end of March to mid April
Vocabulary Quiz - April 15
Please check your science journal for a list of 20 words over Physics (should be around page 144)
Lately we have been studying Physics (the study of forces and motion).
You should know how to apply the definitions of force to motion of objects. The rate of motion is measured as speed. We have different labs including toys to measure the distance and time an object takes and using this to calculate speed.
You will need to be able to graph speed as well.


Please check your science journal for a list of 20 words over Physics (should be around page 144)
Lately we have been studying Physics (the study of forces and motion).
You should know how to apply the definitions of force to motion of objects. The rate of motion is measured as speed. We have different labs including toys to measure the distance and time an object takes and using this to calculate speed.
You will need to be able to graph speed as well.


Thursday, March 21, 2013
Spring Break to end of March
Energy Test Review - Benchmark March 28
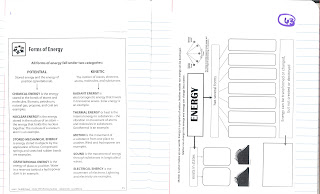
Energy is the ability to do work. Energy can be divided into two main states: kinetic (energy in motion) and potential (energy that is waiting or stored). These two states of energy can be divided into several forms of energy: Mechanical, Radiant, Sound, Chemical, Heat/Thermal, Electrical and Nuclear (MRS CHEN).
Energy can’t be destroyed or created, simply transformed from one form to another. We harness this transforming ability to power our homes with electricity. We can use different energy resources to generate electricity (generally by creating steam, which turns the turbine, which turns the generator). Energy resources may be renewable or nonrenewable.
Think about and be able to answer the following AT MINIMUM:
1. Where does a roller-coaster have the most potential energy (remember this is the same as the least kinetic)? Kinetic energy is based on mass [more mass = more KE]
2. List advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric dams, geothermal, windmills, solar, nuclear, fossil fuels
3. Be able to describe energy transformations in: a) hand-held devices such as radios or flashlight or b) electrical devices like video games c) photosynthesis and d) glow sticks
EX: Flashlight – chem (battery) à electrical (wires) à light
4. Be able to give examples and define all 3 forms of heat transfer:
Heat travels in all directions but moves from warm to cool
a. Convection
b. Conduction
c. Radiation
5. Be able to describe key parts of an energy plan for home and school like the 3 Rs: reduce, reuse, recycle OR turn off lights and appliances at home to save energy use
6. Give examples of different energy resources:
a. geothermal energy: Geyser b. nuclear energy: power plant or the sun
Tuesday, March 5, 2013
March 4- spring break
We are still in our energy unit,but we are incorporating ideas that energy transformations happen all around us every day.
We demonstrated that with several labs and a lab practical using some of these items. Your student should be able to explain the transfer for each item shown below.
We are also adding knowledge of different energy-producing resources that may be used to produce electricity.
Electricity is, simply, produced when a fuel source turns a turbine and generator, moving electricity (electrons) to a battery or outlet for use. Different fuel sources (resources) may be used to produce the mechanical energy necessary to turn the turbine.
We are researching and debating the advantages and disadvantages of different resources, including:
fossil fuels
nuclear power
biomass
hydropower
solar
wind
geothermal
We demonstrated that with several labs and a lab practical using some of these items. Your student should be able to explain the transfer for each item shown below.
We are also adding knowledge of different energy-producing resources that may be used to produce electricity.
Electricity is, simply, produced when a fuel source turns a turbine and generator, moving electricity (electrons) to a battery or outlet for use. Different fuel sources (resources) may be used to produce the mechanical energy necessary to turn the turbine.
We are researching and debating the advantages and disadvantages of different resources, including:
fossil fuels
nuclear power
biomass
hydropower
solar
wind
geothermal
Sunday, February 24, 2013
Feb 25 - March 1
This week we are planning to incorporate all forms of energy into our study, not just Heat or Thermal Energy. Each form of energy will fit under either POTENTIAL or KINETIC energy forms.
We will use the phrase MRS CHEN to remember all the forms
M - mechanical (KE)
R - radiant (KE)
S - sound (KE)
C - chemical (PE)
H - heat (KE)
E - electrical (KE)
N - nuclear (PE)
This study is leading to the understanding that each form of energy transforms into other forms of energy very easily.
For example:
A blow dryer converts electrical energy into heat and sound energy.
A turbine converts heat into mechanical energy which in turn becomes electrical energy.
Our week was filled with mini labs using toys to demonstrate the energy changes when using toys and everyday objects.
We will use the phrase MRS CHEN to remember all the forms
M - mechanical (KE)
R - radiant (KE)
S - sound (KE)
C - chemical (PE)
H - heat (KE)
E - electrical (KE)
N - nuclear (PE)
This study is leading to the understanding that each form of energy transforms into other forms of energy very easily.
For example:
A blow dryer converts electrical energy into heat and sound energy.
A turbine converts heat into mechanical energy which in turn becomes electrical energy.
Our week was filled with mini labs using toys to demonstrate the energy changes when using toys and everyday objects.
February 10-22
In this time, we finished studying about kinetic and potential energy.
We had a lab using a curly cue to demonstrate convection and a lab melting chocolate chips to mainly demonstrate conduction, but we tied in all 3 ways to transfer heat.
We also began and ended a focus on the energy form thermal or heat energy (a subsection of kinetic energy). We discussed the 3 ways that heat can travel: conduction, convection and radiation.
We had a lab using a curly cue to demonstrate convection and a lab melting chocolate chips to mainly demonstrate conduction, but we tied in all 3 ways to transfer heat.
Friday, February 8, 2013
February 4 - 8
This week we started studying Physics. This will be a long unit covering the states and forms of energy and how energy relates to matter in motion (speed).
This week we started with the two major groups of energy--kinetic and potential energy---and the Law of Conservation of Energy.
This week we started with the two major groups of energy--kinetic and potential energy---and the Law of Conservation of Energy.
We demonstrated the greatest amount of potential energy differs by object, but it is based on the position and mass of an object. Kinetic energy is the energy of matter in motion.
Vocabulary and cover page
to be completed as we go through different forms of energy
notes on KE and PE
Monday, January 7, 2013
January 5 - 22
This week we will begin the study of cells and cell theory.
There is no school on Friday.
Life Science topics covered
All living things are based on cells. There are two main types of cells - prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
Complex organisms such as humans (animals), plants, fungi and protists are based on eukaryotic cells with a nucleus and organelles.
Bacteria use prokaryotic cells (no nucleus).
3 Domains - Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya
The 3 Domains are divided into 6 kingdoms - Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, and Protista
Students need to be aware the the key concepts for each taxonomic division (kingdom) include:
the number of cells: whether the organism is multicellular or unicellular
the type of cells: prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic
the type of reproduction: asexual (budding, fragmentation, fission) or sexual (fertilization)
and the method of food gathering: autotrophic or heterotropic
There is no school on Friday.
Life Science topics covered
All living things are based on cells. There are two main types of cells - prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
Complex organisms such as humans (animals), plants, fungi and protists are based on eukaryotic cells with a nucleus and organelles.
Bacteria use prokaryotic cells (no nucleus).
3 Domains - Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya
The 3 Domains are divided into 6 kingdoms - Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, and Protista
Students need to be aware the the key concepts for each taxonomic division (kingdom) include:
the number of cells: whether the organism is multicellular or unicellular
the type of cells: prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic
the type of reproduction: asexual (budding, fragmentation, fission) or sexual (fertilization)
and the method of food gathering: autotrophic or heterotropic
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)